Contents Catalog
The magnesium series products developed with dolomite as raw material play an extremely important role in economic construction and social development. They are mainly used in chemical building materials, refractory materials, sealing materials, electrical insulation materials, advanced ceramic materials and other fields.
Development and application of dolomite
Production of magnesium products
(1) Magnesium smelting industry
The methods of producing magnesium from dolomite are mainly divided into electrolysis and silicothermic method (Pijeng method). The electrolysis method consumes a lot of electricity, has high cost, strict process requirements, complex process, and produces a large amount of chlorine, which is not conducive to environmental protection. The silicothermic method mainly refers to the Pijiang method. At present, in China, the Pijiang method is generally used to smelt magnesium metal because of the easy availability of raw materials, relatively low cost, flexible production scale, and easy-to-master technology.
The main process flow of magnesium smelting by the Pijiang method is: dolomite is calcined and crushed into powder, mixed with ferrosilicon powder and fluorite powder to form a mass, reduced under vacuum conditions to produce crude magnesium, and then refined with flux, cast ingots, and surface treated to obtain finished magnesium ingots. In my country, the Pijiang method for magnesium smelting is widely used, but it also has disadvantages such as blind plant construction, large dolomite consumption, and inadequate treatment of reduction slag that pollutes the environment. Technical management should be strengthened to reduce product costs, realize automated operations, and improve labor productivity.
(2) Production of magnesium carbonate
Magnesium carbonate is an important product among magnesium salts. At present, the magnesium carbonate products produced from dolomite mainly include light magnesium carbonate, spherical magnesium carbonate and transparent magnesium carbonate.
(3) Production of magnesium sulfate
Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate crystals (MgSO4·7H2O) are an important chemical raw material. They are used as fertilizers in agriculture and are widely used in food, feed, cement, printing and dyeing, medicine and other industries. Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate can be divided into reagent grade, pharmaceutical grade, food grade, feed grade, industrial grade, fertilizer grade and other specifications according to different uses. Magnesium sulfate is produced from dolomite as raw material. The method is to calcine dolomite at high temperature, mix it with sulfuric acid of a certain mass concentration in a certain proportion, separate and concentrate magnesium sulfate and calcium sulfate according to the different characteristics of the solubility of the product at various temperatures, and change the temperature conditions to further precipitate impurities such as calcium sulfate. The magnesium sulfate solution is cooled and crystallized to obtain magnesium sulfate crystals. At the same time, the by-product CaSO4·H2O can be obtained. The product purity is relatively high.
(4) Production of magnesium oxide
Magnesium oxide is one of the important basic raw materials for inorganic chemical industry. As a filler, it is widely used in rubber, ceramics, wires and cables and other industries. In addition, magnesium oxide is also an indispensable refractory material. The new processes for extracting magnesium oxide from dolomite mainly include dolomite carbonization method, brine-dolomite method, acid hydrolysis method, ammonium leaching method, etc.
Refractory materials
Refractory materials generally refer to inorganic non-metallic materials with a refractoriness of more than 1580℃. They include natural ores and various products made according to certain requirements and processes. They have high-temperature mechanical properties and good volume stability and are essential materials for various high-temperature equipment. Refractory materials are important basic materials for high-temperature industries and are closely related to the development of industries such as steel, non-ferrous metals, building materials, light industry electronics and chemicals.
Dolomite is calcined at 900℃~1100℃ to obtain a mixture of CaO and MgO called light-burned dolomite. It is highly active and easy to hydrate, which affects its dosage and performance. The two-step calcination method is often used to calcine and sinter light-burned dolomite for a second time to improve its water resistance and prevent cracking and pulverization. Dolomite sand with a lower sintering temperature and higher density can also be produced by mechanical and additive activation methods. Refractory materials made of dolomite are mainly used for steelmaking converter linings, open-hearth furnaces, electric furnace walls, and secondly for thermal equipment such as external refining devices and cement kilns.
Application in the building materials industry
(1) Magnesium cementitious materials
Magnesium cementitious materials have been widely used in the production of interior partition materials, corrugated roof tiles, packaging box profiles for large electromechanical equipment, interior decoration materials, etc. When dolomite is calcined at around 700~800, MgCO3 can be decomposed to produce MgO as the raw material of cementitious materials, and CaCO3 with stable chemical properties can be used as filler. Mixing active MgO with MgCl2 aqueous solution can produce high-strength magnesium oxychloride cement products, which can also be used to produce magnesium hydroxide cement and magnesium sulfate cement.
Dolomite decomposes into two main phases, CaO and MgO, after calcination. Among them, free CaO has a large early expansion coefficient, and MgO has a large late expansion coefficient. Therefore, when the temperature drop causes the volume shrinkage of large-volume concrete, the late expansion effect of MgO can greatly offset this shrinkage. The expansive cement developed from dolomite does not require the addition of other expansion agents. Therefore, dolomite is currently being used to develop expansive cement in the building materials industry.
(2) Glass and ceramic industrial production
Dolomite can provide the CaO and MgO components required for glass manufacturing, among which CaO can act as a flux in the soda-ash-siliceous system. In addition, dolomite can reduce glass aging, prevent chemical erosion caused by the atmosphere or moisture, improve the plasticity of colored glass, and increase glass strength.
In ceramic production, CaCO3 and MgO introduced by dolomite are usually used in ceramic blanks and glazes to replace talc and calcite. In addition, MgO can reduce the blank and firing temperature, promote the dissolution of quartz and the formation of mullite phase, increase the amount of quartz, and reduce the amount of feldspar, thereby increasing the transparency of the blank; because dolomite is a complex salt mineral, glazes with dolomite added are more resistant to smoke and have less crystallization.
Production of dolomite powder
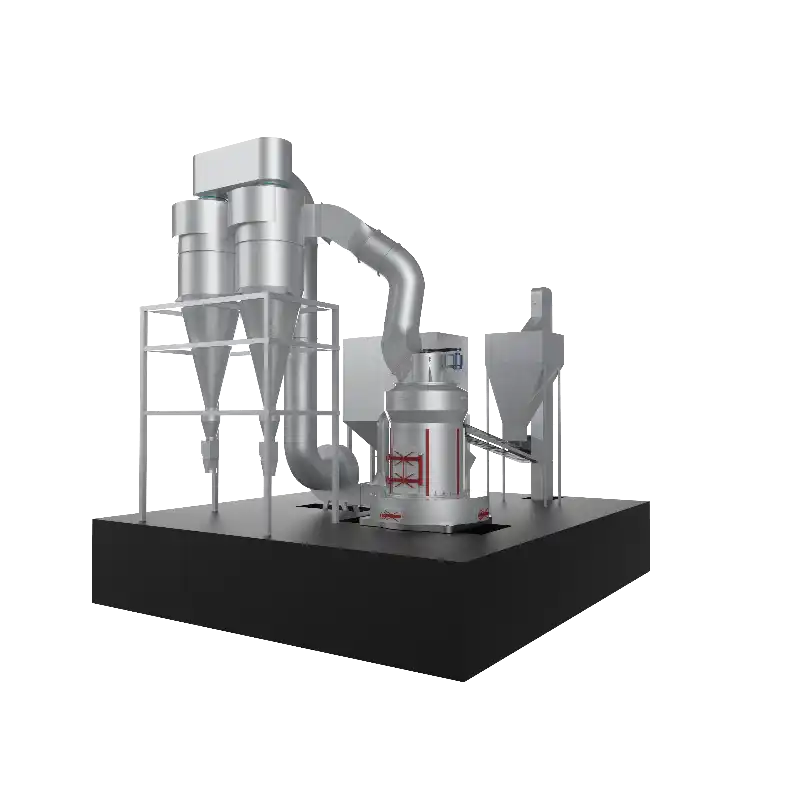
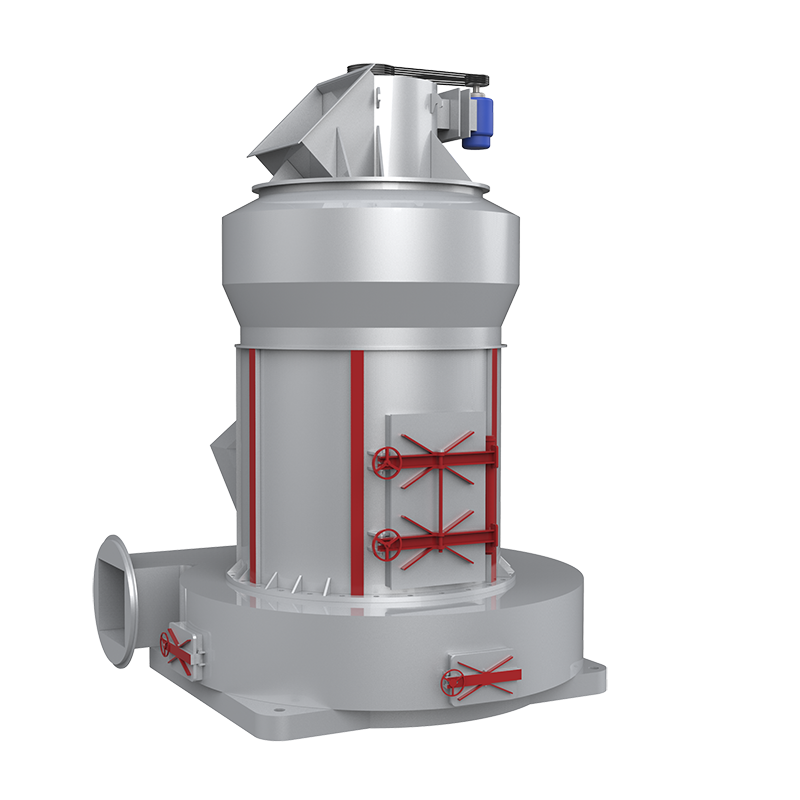
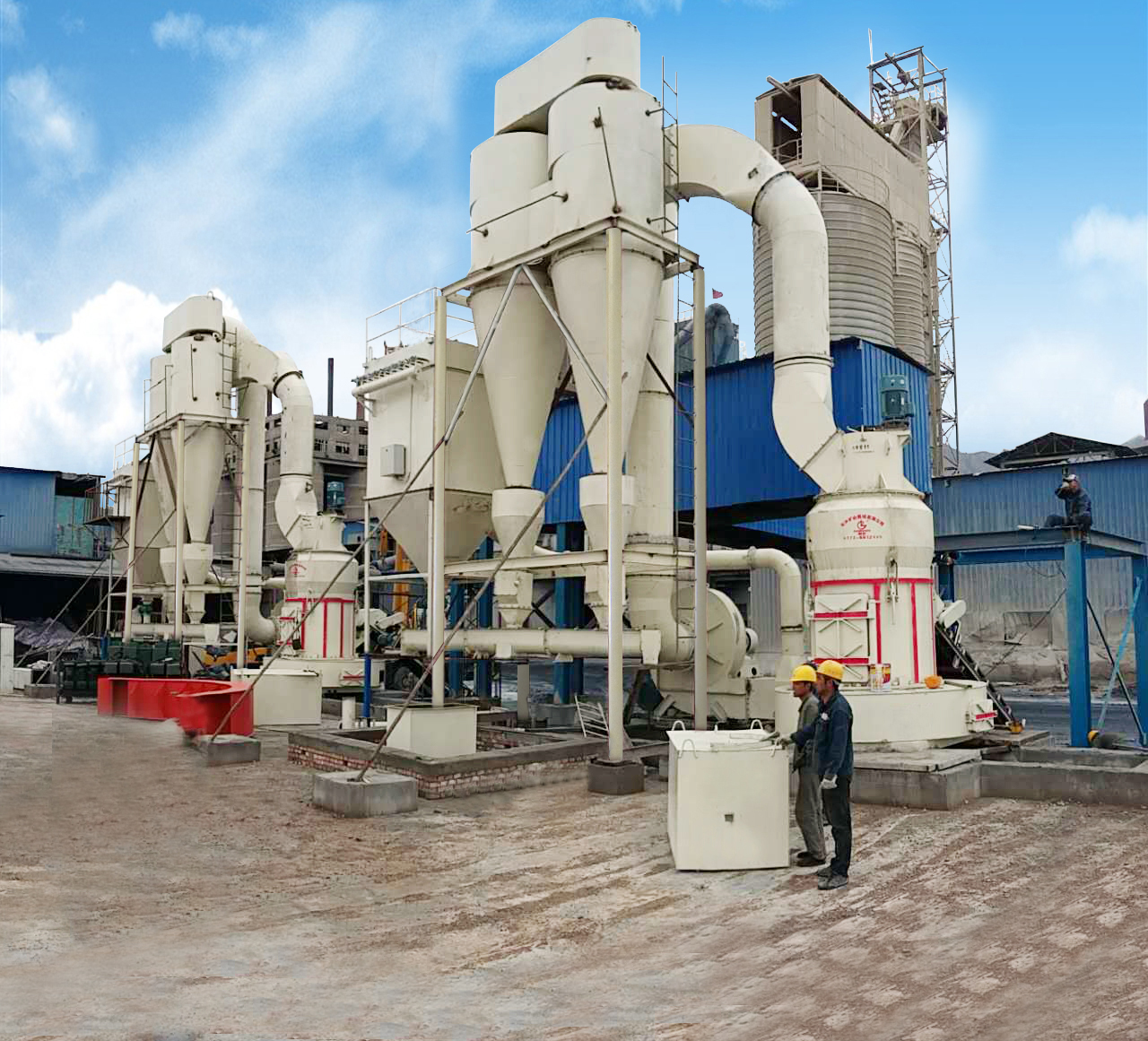
Dolomite can be directly crushed to a certain particle size to make dolomite powder, which is mostly used as filler in rubber, plastic and coating industries. It can also be used as a desulfurizer, flue gas desulfurizer, etc. after adding additives. There are two methods for producing dolomite powder products: dry method and wet method. The dry method is to directly mechanically crush dolomite to a certain particle size after mineral processing, removal of red veins and water washing of mud, or directly apply it, or surface treat it to become an active dolomite powder material. The wet method is to feed dolomite powder of a certain particle size into a wet grinder, add a trace amount of grinding aids to grind it in a water suspension state, and produce an ultrafine powder product.
(1) Application in papermaking
The crystal structure of dolomite is similar to that of calcite. It is low in price and has a high opacity. After wet grinding, it can partially replace heavy calcium carbonate as a papermaking filler or be used to prepare composite materials, improve the performance of paper, make more reasonable and effective use of resources, and reduce costs.
Liu Yin et al. added a certain amount of ultrafine dolomite powder to the Ca(OH)2-H2O-CO2 system and modified it by nano-coating. The modified dolomite was used as a papermaking filler, and the tensile index, burst index, tear index, folding endurance and retention rate of the finished paper were all improved. Dolomite powder can be obtained by sorting, crushing and grinding dolomite ore, which can replace light calcium powder or heavy calcium powder in rubber, coating, plastic and other industries to a certain extent, and has broad development prospects.
(2) Application in agriculture
Dolomite can be used as magnesium fertilizer to provide the medium element magnesium necessary for the growth of crops, and the 0.8~1.2µm dolomite particles can flow freely. Used as a fertilizer filler, it can improve the conditions for plants to absorb and utilize soil nutrients, reduce caking, and facilitate the adjustment of fertilizer ratios. Dolomite powder is alkaline and can be directly added to urea fertilizer to adjust the soil pH value, which can increase crop yields by 15%~40% and improve the efficacy of herbicides.
(3) Application in coatings
Dolomite is processed through water selection, drying, crushing, grinding, grading and other processes, and then chemically treated, surface treated, pH value adjusted, rinsed and other processes to produce a new type of pigment. Its chemical composition is stable, and it has many advantages such as weather resistance, corrosion resistance, fine powder, easy dispersion, high whiteness, low cost, and unique process, and can be used in various paints. The produced coating has the characteristics of being able to reduce the amount of titanium dioxide, high hardness, good hand feel, good fluidity, and strong adhesion, and the application effect is better than that of heavy calcium carbonate.
(4) Application in water treatment
The acidic wastewater treatment method usually uses neutralization method first. Dolomite powder can be used as a filter material for water treatment, especially for neutralization treatment from drinking water to industrial water and swimming pool water. In addition, research on using dolomite powder to treat wastewater containing heavy metals such as iron, manganese, chromium, and lead is in-depth.