Contents Catalog
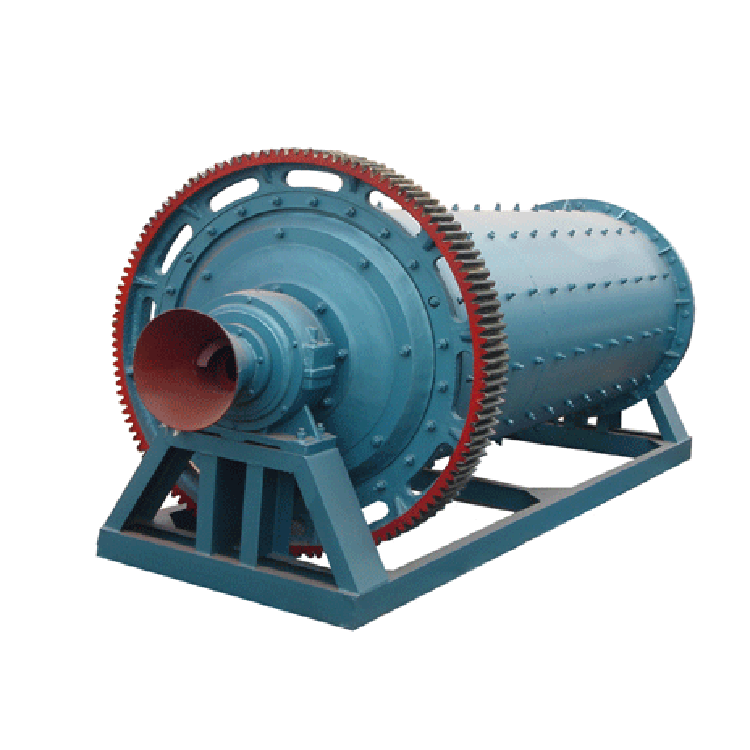
Ball Mill Introduction
The ball mill is a key equipment for crushing materials after they have been crushed. Ball mills are widely used in cement, silicate products, new building materials, refractory materials, fertilizers, black and non-ferrous metal beneficiation, and glass ceramics, for dry or wet grinding of various ores and other grindable materials.

Working Principle Of Ball Mill
This machine is a skeleton ball mill driven by horizontal cylindrical turning gears, external gears, and two hoppers. The material enters the first hopper through the hollow shaft screw of the feeding equipment. The hopper has a trapezoidal or corrugated sheath, which contains steel balls that fall under the centrifugal force of the cylinder to grind the material. After rough grinding in the first hopper, the material enters the second hopper through a single-layer partition. The second hopper has a flat scale plate with steel balls for grinding the material. The powder is discharged from the grid plate to complete the grinding process.4
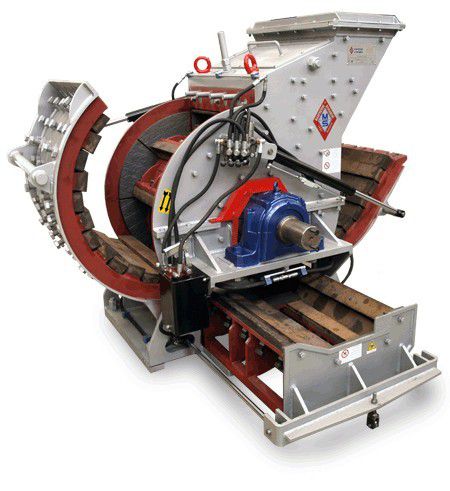
Composition elements of Ball Mill

Equipment model of Cronus Ball Mill
| 型号 model | 筒体转速 Cylinder rotation speed (r/min) | 装球量 ball load (T) | 给料粒度 Feed particle size(mm) | 出料粒度 Discharge size (mm) | 电机功率Motor Power(kw) | 产量production (T/H) | 重量weight(T) |
| 900*1800 | 37 | 1.8 | ≤15 | 0.075-0.4 | 15 | 0.5-2 | 3.4 |
| 900*2100 | 37 | 2.3 | ≤15 | 0.075-0.4 | 18.5 | 0.4-2 | 3.9 |
| 900*3000 | 35 | 3.85 | ≤25 | 0.075-0.4 | 30 | 1.1-2.5 | 7.78 |
| 1200*2400 | 35 | 4.6 | ≤25 | 0.075-0.4 | 30 | 1.3-3.2 | 8.65 |
| 1200*2800 | 35 | 5.4 | ≤25 | 0.075-0.4 | 37 | 1.5-3.7 | 10.02 |
| 1200*4500 | 35 | 8.6 | ≤25 | 0.075-0.4 | 45 | 2.7-6.79 | 14 |
| 1500*3000 | 29 | 9 | ≤25 | 0.047-0.4 | 75 | 3.3-8.2 | 14.12 |
| 1500*3500 | 29 | 10.5 | ≤25 | 0.047-0.4 | 75 | 3.3-8.5 | 15.64 |
| 1500*4500 | 29 | 13.5 | ≤25 | 0.047-0.4 | 90 | 4.5-12 | 20 |
| 1500*5700 | 29 | 17 | ≤25 | 0.047-0.4 | 110 | 2.6-14 | 21.5 |
| 1830*3000 | 24 | 13.5 | ≤25 | 0.047-0.4 | 135 | 4-15 | 28 |
| 1830*3600 | 24 | 14 | ≤25 | 0.047-0.4 | 135 | 4-15 | 29 |
| 1830*4500 | 24 | 20 | ≤25 | 0.047-0.4 | 155 | 4-19 | 32 |
| 1830*7000 | 24 | 31.5 | ≤25 | 0.047-0.4 | 210 | 6-22 | 36.5 |
| 2100*3000 | 22 | 18 | ≤25 | 0.047-0.4 | 210 | 6.4-28 | 40.79 |
| 2100*3600 | 22 | 20 | ≤25 | 0.047-0.4 | 210 | 7-28 | 42 |
| 2100*4000 | 22 | 21.5 | ≤25 | 0.047-0.4 | 210 | 7.6-28 | 43.45 |
| 2200*3600 | 21.7 | 25 | ≤25 | 0.047-0.4 | 245 | 5.2-32 | 44 |
| 2200*7000 | 21.7 | 46 | ≤25 | 0.047-0.4 | 380 | 15-38 | 63 |
| 2400*3600 | 21 | 28 | ≤25 | 0.047-0.4 | 320 | 8-60 | 47 |
| 2400*4500 | 21 | 35 | ≤25 | 0.047-0.4 | 380 | 8.5-60 | 70.5 |
| 2400*7500 | 20.8 | 38 | ≤25 | 0.047-0.4 | 475 | 30-42 | 86 |
| 2700*3600 | 20.7 | 40 | ≤25 | 0.047-0.4 | 400 | 12-80 | 93 |
| 2700*4500 | 20.7 | 48 | ≤25 | 0.047-0.4 | 430 | 12-90 | 102 |
| 3000*4500 | 20.7 | 55 | ≤25 | 0.047-0.4 | 580 | 50-105 | 107 |
| 3000*9000 | 20.7 | 75 | ≤25 | 0.047-0.4 | 800 | 80-90 | 156 |
| 3200*3600 | 18 | 55 | ≤25 | 0.047-0.4 | 630 | 60-120 | 118 |
| 3200*4500 | 18 | 65 | ≤25 | 0.047-0.4 | 800 | 30-180 | 137 |
Advantages of Ball Mill Compared to Raymond Mill or Ultra-fine Grinding Mill:
- Versatility in Grinding: Ball mills can handle a wide range of materials, from soft to extremely hard and brittle substances. They are capable of both dry and wet grinding processes, making them more versatile than Raymond mills, which are typically limited to dry grinding.
- Particle Size Control: Ball mills offer better control over the final particle size distribution. By adjusting the size of the grinding media, the rotation speed, and the grinding time, operators can achieve a more uniform and finer product compared to Raymond mills, which may struggle with achieving ultra-fine particle sizes.
- Higher Capacity: Ball mills generally have a higher grinding capacity, making them suitable for large-scale production. In contrast, Raymond mills and ultra-fine grinding mills are often limited in throughput, making them less efficient for high-volume operations.
- Durability and Low Maintenance: Ball mills are robust and durable, with fewer moving parts compared to Raymond mills. This results in lower maintenance requirements and longer operational lifespans. Additionally, the grinding media in ball mills can be easily replaced, whereas the rollers and rings in Raymond mills may wear out more quickly and require more frequent maintenance.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Although the initial investment in a ball mill may be higher, its long-term operational costs are often lower due to its durability, lower maintenance needs, and higher efficiency. Raymond mills and ultra-fine grinding mills may incur higher maintenance and replacement costs over time.
- Adaptability to Various Conditions: Ball mills can operate under a wide range of conditions, including high temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for more demanding industrial applications. Raymond Mills, on the other hand, may have limitations in such environments.